What is the Difference Between Industrial and Consumer 3D Printers?
Manufacturing, product development, and even hobby projects have been transformed by 3D printing technology. But not every 3D printer is created equal. Consumer (desktop) and industrial 3D printers are the two primary categories. Businesses can choose the best investment if they know how they differ from one another.
To help you choose the type that best meets your needs, we'll break down the main differences in this article based on performance, materials, cost, applications, and scalability.
1. Effectiveness and Accuracy
Important characteristics: Greater resolution (smoother surfaces and finer details)
Increased printing speeds (designed for mass production)
Improved reliability (reliable performance during extended print jobs)
Consumer 3D Printers: Ideal for Hobby and Prototyping Use
Consumer-grade 3D printers are less expensive, but they give up some speed and accuracy. They are perfect for hobbyists, small enterprises, and teaching.
Important characteristics:
Reduced resolution (prints with visible layer lines)
slower rates (not mass-production optimised)
Limited reproducibility (printing may differ slightly from job to job)
2. Compatibility of Materials
3D printers for industry: Encourage the Use of High-Performance and Advanced Materials
Engineering-grade metals, composites, ceramics, and thermoplastics can all be handled by industrial machinery. Among the examples are:
PEEK, nylon, and ULTEM (resistant to chemicals and heat)
Aluminium, titanium, and stainless steel (for metal components)
Materials reinforced with carbon fibre (for added strength)
Industrial 3D printers can produce functioning end-use parts in harsh conditions thanks to these materials.
3D printers for consumers: restricted to simple plastics
PLA, ABS, PETG, and occasionally TPU are compatible with the majority of consumer 3D printers. These materials are excellent for toys, prototypes, and ornamental objects, but they are not durable enough for use in industrial settings.

3. Increase Scalability and Volume
Large-Scale Production Capabilities of Industrial 3D Printers
Businesses can print larger parts or more components at once since industrial machines frequently have higher build volumes. In order to minimize manual intervention, several industrial technologies also provide automated batch manufacturing.
Smaller and Manually Operated Consumer 3D Printers
The construction sizes of desktop 3D printers are typically less than 300x300x300 mm. They are not the best for bulk production and need constant user supervision.
Depending on the technology, prices might range from 10,000 to more than one million dollars.
Over time, increased efficiency lowers labour expenses and material waste.
increased return on investment for companies that require high-quality, useful parts.
Low-cost, low-return consumer 3D printers
The price range is between 200 and 5,000.
Slower rates and material constraints result in higher costs per part.
Ideal for amateurs or low-volume prototypes.
5. Use Cases for Industrial 3D Printing: Where Each Type Succeeds
Aerospace: Components that are strong and lightweight
Medical: Personalised implants and instruments for surgery
Automotive: Sturdy, useful components and jigs
Manufacturing: Final components for manufacturing
Use Cases for Consumer 3D Printing
Creating rapid concept models for prototyping
Education: Teaching the fundamentals of 3D printing
Hobbyists: Personalized home décor, toys, and figurines
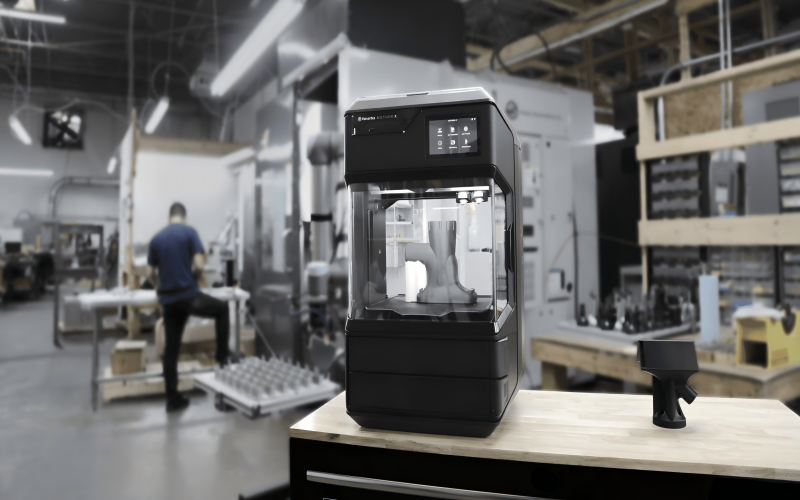

What Should You Pick?
If you require an industrial 3D printer, pick one:
✔ High accuracy and consistency
✔Advanced materials (high-performance polymers, metal)
✔ Automated or large-scale manufacturing
✔ Useful final components
Select a consumer 3D printer if you require:
✔ inexpensive prototyping
✔ hobby or small-scale projects
✔ simple plastic materials
Concluding remarks
Your budget, output requirements, and material needs will all influence your decision between industrial and consumer 3D printers. Consumer models are excellent for learning and modest projects, while industrial 3D printers provide businesses with higher performance.
Hstar offers dependable solutions customized for your sector if you're searching for a top-notch industrial 3D printer to increase your manufacturing capabilities. For a consultation, contact us right now!
To help you choose the type that best meets your needs, we'll break down the main differences in this article based on performance, materials, cost, applications, and scalability.
1. Effectiveness and Accuracy
3D printers for industry: High Accuracy & Speed
Industrial 3D printers are made to be extremely accurate, repeatable, and able to produce at high speeds. They are frequently employed in the heavy manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and medical sectors where precise tolerances—often within microns—are essential. Important characteristics: Greater resolution (smoother surfaces and finer details)
Increased printing speeds (designed for mass production)
Improved reliability (reliable performance during extended print jobs)
Consumer 3D Printers: Ideal for Hobby and Prototyping Use
Consumer-grade 3D printers are less expensive, but they give up some speed and accuracy. They are perfect for hobbyists, small enterprises, and teaching.
Important characteristics:
Reduced resolution (prints with visible layer lines)
slower rates (not mass-production optimised)
Limited reproducibility (printing may differ slightly from job to job)
2. Compatibility of Materials
3D printers for industry: Encourage the Use of High-Performance and Advanced Materials
Engineering-grade metals, composites, ceramics, and thermoplastics can all be handled by industrial machinery. Among the examples are:
PEEK, nylon, and ULTEM (resistant to chemicals and heat)
Aluminium, titanium, and stainless steel (for metal components)
Materials reinforced with carbon fibre (for added strength)
Industrial 3D printers can produce functioning end-use parts in harsh conditions thanks to these materials.
3D printers for consumers: restricted to simple plastics
PLA, ABS, PETG, and occasionally TPU are compatible with the majority of consumer 3D printers. These materials are excellent for toys, prototypes, and ornamental objects, but they are not durable enough for use in industrial settings.

3. Increase Scalability and Volume
Large-Scale Production Capabilities of Industrial 3D Printers
Businesses can print larger parts or more components at once since industrial machines frequently have higher build volumes. In order to minimize manual intervention, several industrial technologies also provide automated batch manufacturing.
Smaller and Manually Operated Consumer 3D Printers
The construction sizes of desktop 3D printers are typically less than 300x300x300 mm. They are not the best for bulk production and need constant user supervision.
4. Cost: Upfront Expense against Future Gains
Industrial 3D Printers: Lower Cost Per Part, Higher Upfront CostDepending on the technology, prices might range from 10,000 to more than one million dollars.
Over time, increased efficiency lowers labour expenses and material waste.
increased return on investment for companies that require high-quality, useful parts.
Low-cost, low-return consumer 3D printers
The price range is between 200 and 5,000.
Slower rates and material constraints result in higher costs per part.
Ideal for amateurs or low-volume prototypes.
5. Use Cases for Industrial 3D Printing: Where Each Type Succeeds
Aerospace: Components that are strong and lightweight
Medical: Personalised implants and instruments for surgery
Automotive: Sturdy, useful components and jigs
Manufacturing: Final components for manufacturing
Use Cases for Consumer 3D Printing
Creating rapid concept models for prototyping
Education: Teaching the fundamentals of 3D printing
Hobbyists: Personalized home décor, toys, and figurines

What Should You Pick?
If you require an industrial 3D printer, pick one:
✔ High accuracy and consistency
✔Advanced materials (high-performance polymers, metal)
✔ Automated or large-scale manufacturing
✔ Useful final components
Select a consumer 3D printer if you require:
✔ inexpensive prototyping
✔ hobby or small-scale projects
✔ simple plastic materials
Concluding remarks
Your budget, output requirements, and material needs will all influence your decision between industrial and consumer 3D printers. Consumer models are excellent for learning and modest projects, while industrial 3D printers provide businesses with higher performance.
Hstar offers dependable solutions customized for your sector if you're searching for a top-notch industrial 3D printer to increase your manufacturing capabilities. For a consultation, contact us right now!
RECENT POSTS
Application
-
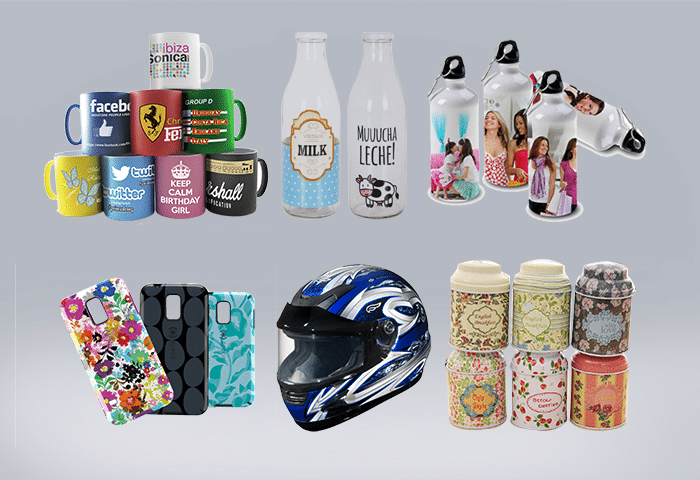 Application scenarios of UV DTF printersUV DTF printer is our NEW machine, which is loved by many consumers.crystal stickers are widely used.
Application scenarios of UV DTF printersUV DTF printer is our NEW machine, which is loved by many consumers.crystal stickers are widely used.
Crystal stickers can also be used as decorations to make your gift more beautiful and special. -
 DTF Printer Effect ShowDirect to film printer(DTF printers) are T-shirt transfer printers,Hstar DTF printer offer a transfer solution especially for dark color fabric,which is a creative application process.
DTF Printer Effect ShowDirect to film printer(DTF printers) are T-shirt transfer printers,Hstar DTF printer offer a transfer solution especially for dark color fabric,which is a creative application process.
More Application







.jpg)